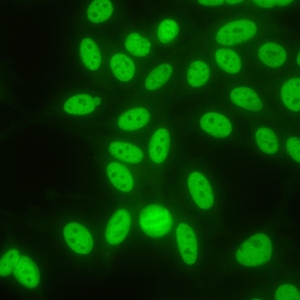
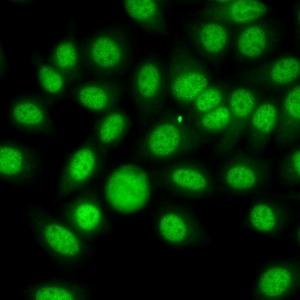
Padrão não encontrado!
- Nucleolares
Descrição
Associação Antigênica
Doença Associada
Relevância Clínica (Primeiro Nível)
Present to a varying degree in distinct SARD, in particular SjS, SLE, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, neonatal lupus erythematosus, congenital heart block, DM, SSc, and SSc-AIM overlap syndrome.
If SjS, SLE, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, neonatal lupus erythymatosus, or congenital heart block is clinically suspected, it is recommended to perform follow-up tests for anti-SS-A/Ro (Ro60) and anti-SS-B/La antibodies; in most laboratories these antigens are included in the routine ENA profile.
Autoantibodies to SS-A/Ro are part of the classification criteria for SjS (the criteria do not distinguish between Ro60 and Ro52/TRIM21).
If SSc, AIM, or to a lesser extend SLE, is clinically suspected, it is recommended to perform follow-up tests for detecting autoantibodies to Mi-2, TIF1?, and Ku; these antigens are typically included in disease specific immunoassays (i.e., inflammatory myopathy profile).
Autoantibodies to Mi-2 and TIF1? are associated with DM; autoantibodies to TIF1? in patients with DM, although rare in the overall AC-4 pattern, is strongly associated with malignancy in old patients.
Autoantibodies to Ku are associated with SSc-AIM and SLE-SSc-AIM overlap syndromes.
Anti-SS-A/Ro (Ro60) and AIM-specific autoantibodies may be undetected in HEp-2 IIFA-screening.