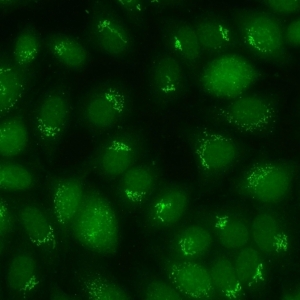
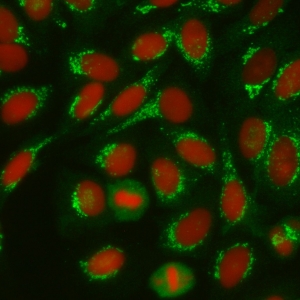
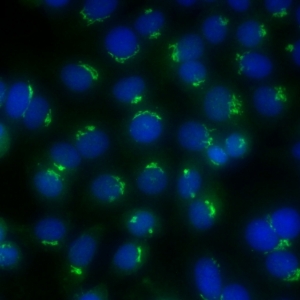
AC-22 - POLAR/GOLGI-like
Descrição
Discontinuous speckled or granular perinuclear ribbon-like staining with polar distribution in the cytoplasm. e.g. anti-giantin, anti-golgin-245.
Associação Antigênica
giantin/macrogolgin, golgin-95/GM130, golgin-160, golgin-97, golgin-245
Doença Associada
rare in SjS, SLE, RA, MCTD, GPA, idiopathic cerebellar ataxia, paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, viral infections
Relevância Clínica (Primeiro Nível)
Found in small numbers of patients with a variety of conditions
Antigens recognized include giantin/macrogolgin and distinct golgin molecules; specific immunoassays to detect autoantibodies directed to specific Golgi antigens are currently not commercially available
Relevância Clínica (Segundo Nível)
The AC-22 pattern has been reported in small numbers of patients with a variety of conditions, including SjS, SLE, RA, MCTD, GPA, idiopathic cerebellar ataxia, paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, adult Still’s disease, and viral infections including HIV and EBV
Although possibly biased by the referral pattern, one study concluded that the AC-22 pattern is not clinically associated with SARD as there were only 1 SjS and 2 RA diagnoses among their 20 AC-22 positive cases collected over 10-years and a clinical follow-up observation ranging from 0 – 10 years; the remaining cases showed diverse diagnoses including 2 carcinomas
The AC-22 pattern is rare in the general population
Referências
Stinton LM, Eystathioy T, Selak S, et al. Autoantibodies to protein transport and messenger RNA processing pathways: endosomes, lysosomes, Golgi complex, proteasomes, assemblyosomes, exosomes, and GW bodies. Clin Immunol 2004;110:30–44.
Covini G, Carcamo WC, Bredi E, et al. Cytoplasmic rods and rings autoantibodies developed during pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther 2012;17:805–11.
Calise SJ, Keppeke GD, Andrade LE, et al. Anti-rods/rings: a human model of drug- induced autoantibody generation. Front Immunol 2015;6.
Novembrino C, Aghemo A, Ferraris Fusarini C, et al. Interferon-ribavirin therapy induces serum antibodies determining ’rods and rings’ pattern in hepatitis C patients. J Viral Hepat 2014;21:944–9.
Keppeke GD, Calise SJ, Chan EK, et al. Anti-rods/rings autoantibody generation in hepatitis C patients during interferon-?/ribavirin therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:1966–74.
Fritzler MJ, Etherington J, Sokolu, C, et al. Antibodies from patients with autoimmune disease react with a cytoplasmic antigen in the Golgi apparatus. J Immunol 1984;132:2904-8.
Vermeersch P, Van den Bergh K, Blockmans D, et al. Anti-Golgi autoantibodies are not clinically Staub HL, Souza F, Chan EKL, et al. Anti-Golgi antibodies in adult Still's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2003;21:275-6.
Vermeersch P, Van den Bergh K, Blockmans D, et al. Anti-Golgi autoantibodies are not clinically associated with systemic autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70:234-5.
Satoh M, Chan EKL, Ho LA, et al. Prevalence and sociodemographic correlates of antinuclear antibodies in the United States. Arthritis Rheum 2012;64:2319-27.